Compose 使用 Kotlin 語言的宣告式語法,讓開發者能夠以更直觀、更簡潔的方式來構建使用者介面。
Kotlin 協同程式,也是很重要的概念。
提供了一種非同步且輕量級的方式來處理長時間運行的任務,例如網路請求、資料庫操作等,而不阻塞主執行緒。
在主程式直接delay
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
delay(1000)
println("30天")
}
就會噴 error ,就鐵人賽delay 1天,就斷賽一樣
阻塞主執行緒,等待協同程式完成
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
delay(1000)
println("30天")
}
}
iThome鐵人賽
30天
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
printCompetitionDays()
}
}
suspend fun printCompetitionDays() {
delay(1000)
println("30天")
}
iThome鐵人賽
30天
import kotlin.system.*
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
val time = measureTimeMillis {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
printCompetitionDays()
printCompetitionCategory()
}
}
println("Execution time: ${time / 1000.0} seconds")
}
suspend fun printCompetitionDays() {
delay(1000)
println("30天")
}
suspend fun printCompetitionCategory() {
delay(1000)
println("行動開發")
}
iThome鐵人賽
30天
行動開發
執行時間: 2.089 秒
Kotlin 中的協同程式遵循稱為結構化並行的重要概念
啟動一個新的協同程式
使用並行方式執行任務,請在程式碼中新增多個 launch() 函式,以便同時處理多個協同程式。
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
val time = measureTimeMillis {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
launch {
printCompetitionDays()
}
launch {
printCompetitionCategory()
}
}
println("Execution time: ${time / 1000.0} seconds")
}
}
suspend fun printCompetitionDays() {
delay(1000)
println("30天")
}
suspend fun printCompetitionCategory() {
delay(1000)
println("行動開發")
}
iThome鐵人賽
30天
行動開發
執行時間: 1.103 秒
執行時間: 2.089 秒 -> 執行時間: 1.103 秒
fun main() {
val time = measureTimeMillis {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
launch {
printCompetitionDays()
}
launch {
printCompetitionCategory()
}
println("祝你堅持的三十天!")
}
println("Execution time: ${time / 1000.0} seconds")
}
}
....
iThome鐵人賽
祝你堅持的三十天!
30天
行動開發
執行時間: 1.098 秒
會發現為 printCompetitionDays() 和 printCompetitionCategory() 啟動兩個新的協同程式後,就可以繼續處理輸出 祝你堅持的三十天! 的下一個指示了。
用於啟動一個新的協同程式,並 返回一個 Deferred 物件。這個 Deferred 物件代表著這個協同程式的未來結果。我們可以在需要的時候,透過 await() 函式來取得這個結果。
相較於 launch(),async() 更常用於需要取得回傳值的非同步任務。
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
val days: Deferred<String> = async {
getCompetitionDays()
}
val category: Deferred<String> = async {
getCompetitionCategory()
}
println("${days.await()} ${category.await()}")
println("祝你堅持的三十天!")
}
}
suspend fun getCompetitionDays(): String {
delay(1000)
return "30天"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionCategory(): String {
delay(1000)
return "行動開發"
}
iThome鐵人賽
30天 行動開發
祝你堅持的三十天!
平行分解 (Parallel Decomposition) 則是將一個任務拆分成多個子任務,並同時執行這些子任務,以提高效率。在 Kotlin 協同程式中,我們可以利用 async 函式和 CoroutineScope 來輕鬆實現平行分解。
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
println(getCompetitionReport())
println("祝你堅持的三十天!")
}
}
suspend fun getCompetitionReport() = coroutineScope {
val category = async { getCompetitionCategory() }
val days = async { getCompetitionDays() }
"${category.await()} ${days.await()}"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionDays(): String {
delay(1000)
return "30天"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionCategory(): String {
delay(1000)
return "行動開發"
}
iThome鐵人賽
行動開發 30天
祝你堅持的三十天!
如果您知道程式碼的某些部分可能會擲回例外狀況,可以使用 try-catch 區塊包住該程式碼。
有Exception
iThome鐵人賽
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.AssertionError: 忘記寫文章斷賽了
at FileKt.getCompetitionDays (File.kt:61)
at FileKt$getCompetitionDays$1.invokeSuspend (File.kt:-1)
at kotlin.coroutines.jvm.internal.BaseContinuationImpl.resumeWith (ContinuationImpl.kt:33)
解決
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
println(getCompetitionReport())
println("祝你堅持的三十天!")
}
}
suspend fun getCompetitionReport() = coroutineScope {
val category = async { getCompetitionCategory() }
val days = async {
try {
getCompetitionDays()
} catch (e: AssertionError) {
println("斷賽原因 exception $e")
"{ 沒po文 斷賽 }"
}
}
"${category.await()} ${days.await()}"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionDays(): String {
delay(500)
throw AssertionError("忘記寫文章斷賽了")
return "30天"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionCategory(): String {
delay(1000)
return "行動開發"
}
iThome鐵人賽
斷賽原因 exception java.lang.AssertionError: 忘記寫文章斷賽了
行動開發 { 沒po文 斷賽 }
祝你堅持的三十天!
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("iThome鐵人賽")
println(getCompetitionReport())
println("祝你堅持的三十天!")
}
}
suspend fun getCompetitionReport() = coroutineScope {
val category = async { getCompetitionCategory() }
val days = async { getCompetitionDays() }
delay(200)
days.cancel() //決定棄賽
"${category.await()} }"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionDays(): String {
delay(500)
return "30天"
}
suspend fun getCompetitionCategory(): String {
delay(1000)
return "行動開發"
}
iThome鐵人賽
行動開發
祝你堅持的三十天!
代表一個協同程式
可以用來控制協同程式的生命週期,例如啟動、取消、等待完成等。
val job = launch { ... }
job.cancel()
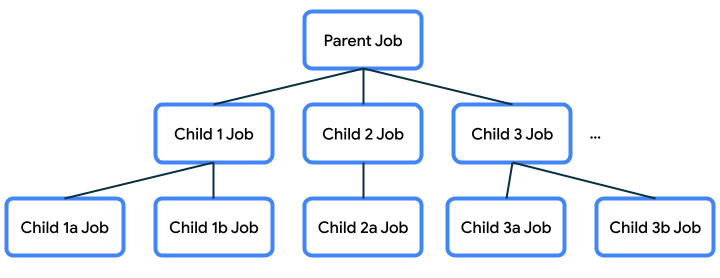
父項/子項關係會為子項、父項以及屬於同一父項的其他子項指定特定行為,因此十分重要。在前面的例子中,我們已透過天氣程式介紹這個行為。
CoroutineContext 可以被視為協同程式的上下文環境,它包含了協同程式執行所需要的一些資訊,例如:
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() = runBlocking {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default)
val job = scope.launch {
try {
delay(500L)
println("Task started")
delay(1500L)
println("Task finished")
} catch (e: CancellationException) {
println("Task was cancelled")
} finally {
println("Cleaning up")
}
}
delay(1300L)
job.cancelAndJoin()
println("Main program finished")
}
Task started
Task was cancelled
Cleaning up
Main program finished
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() {
runBlocking {
println("${Thread.currentThread().name} - runBlocking function")
launch {
println("${Thread.currentThread().name} - launch function")
withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
println("${Thread.currentThread().name} - withContext function")
delay(1000)
println("10 results found.")
}
println("${Thread.currentThread().name} - end of launch function")
}
println("Loading...")
}
}
main @coroutine#1 - runBlocking function
Loading...
main @coroutine#2 - launch function
DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 @coroutine#2 - withContext function
10 results found.
main @coroutine#2 - end of launch function
